Plug Into More Green Stock News
Tap into the pulse of emerging green sectors every morning. Top daily headlines from clean energy, cleantech, cannabis, and sustainable transport stocks:
Sigma Lithium Announces Exceptional PEA Results Supporting Doubling Planned Production Capacity to 440,000tpa (66,000 LCE)
PHASE 2 PRODUCTION HIGHLIGHTS
- Project’s near-term production capacity of battery grade high-purity green lithium will be potentially doubled:
- Production is planned to increase from 220,000 tpa (33,000 LCE) planned for 2022 in Phase 1, to 440,000 tpa (66,000 LCE), within approximately one year.
- Phase 2 production has a projected life of mine of approximately 13 years: vertically integrated to Sigma’s second deposit, Barreiro with 20.5 Mt of measured & indicated high-grade and high-purity lithium resources at 1.43% Li2O.
- Low-risk execution strategy: Phase 2 construction is planned to start once Phase 1 concludes commissioning and ramps up production in 2022.
- The Company has significantly advanced multiple Project workstreams with the objective of preparing for Phase 2 production after 2023.
PHASE 2 FINANCIAL HIGHLIGHTS
- Phase 2 has the potential to more than double total NPV of the Project to US$844 million:
- NPV of Phase 2 Production US$449 million.
- Low initial capital expenditures of US$44.5 million.
- Phase 2 after-tax cash flow generation during 13 years is projected as follows:
- Net revenue of US$2.1 billion (annualized US$165 million).
- After Tax Free Cash Flow of US$ 766 million (annualized US$60 million).
- EBITDA of US$1 billion (annualized US$83 million).
- IRR of 208%.
- Located close to Atlantic emerging supply chain for electric vehicles in North America and Europe, Phase 2 would enable Sigma to continue to be amongst the lowest cost producers in the industry.
- PEA projects Phase 2 average total cash cost to be US$256/t (FOB Plant, life of mine) and US$360/t (CIF China Port, life of mine).
PHASE 1 CONSTRUCTION UPDATE
- All Detailed Engineering and Pre-Construction workstreams continued to advance to achieve production in the third quarter of 2022. https://vimeo.com/554389108 to Video with 3D rendering of Production Plant
- Construction site early works are ongoing (clearing and grubbing, laydowns & topsoil removal).
- Concluded all field Pre-Construction activities for the Production Plant.
- Completed trade-off studies for the optimization and expandability/scalability of the overall plant design, evaluating multiple design options, performing tests and analysis to select the preferred option.
- Concluded the definition of the streamlined scope and design of the non-process, non-plant infrastructure (building infrastructure).
- Completed several critical workstreams involved in the Pre-Construction of the Phase 1 Mine within the scheduled and budgeted parameters, including all field-based activities required for the geotechnical as well as hydrogeological validations.
Sigma Lithium Resources Corporation (“Sigma” or the “Company”) ( TSX-V: SGMA ) ( OTC- QB: SGMLF ) is pleased to announce the exceptional results of a Preliminary Economic Assessment (the “PEA”) for an expansion of its Grota do Cirilo Project (the “Project”), doubling its annual production capacity of battery-grade, high-purity, environmentally sustainable 6% lithium concentrate (“Green Battery Grade Lithium Concentrate”) to approximately 440,000 tpa (66,000 LCE).
The expansion of Project achieves significant operational economies of scale resulting from adding a second environmentally friendly dense media separator processing line train to its digitally automated production plant (the “Production Plant”). The second line is expected to produce an average of 222,000 tpa (33,000 LCE) of Battery Grade Green Lithium Concentrate (“Phase 2”), doubling the initial planned annual production capacity of 220,000tpa (33,000 LCE) (“Phase 1”).
Phase 1 is described in the Sigma’s technical report titled “Grota do Cirilo Lithium Project, Araçuaí and Itinga Regions, Minas Gerais, Brazil, National Instrument 43-101 Technical Report on Feasibility Study Final Report” dated October 18, 2019 (the “2019 Feasibility Study Report”).
The exceptional PEA results demonstrate the cost benefit of vertically integrating the second production line and utilizing as a feedstock spodumene ore from the Project’s second deposit Barreiro (the “Second Deposit” or “Barreiro”), mining an average of 1.68Mt per year during 12.7 years of mine life. Barreiro is a high-purity, high-grade lithium deposit, with 20.485Mt of measured & indicated mineral resources at 1.43% Li2O and 1.909Mt of inferred mineral resources and shallow, near surface mineralization ideal for open pit mining. The Second Deposit’s mineral reserve is expected to be declared later this quarter when the ongoing pre-feasibility study (“PFS”) is completed.
The PEA projects capital expenditures of US$44.5 million (year 0) including plant and mine construction, based on an optimized mine plan. Incremental expenditures of US$28.9 million (additional mine stripping on year 5) and US$9.6 million (additional mine stripping on year 6) is expected to be covered by the Company’s internal cash flow generation. As Phase 2 construction is planned sequentially to the commissioning and production ramp up of Phase 1, the Company is expected to be fully operational with Phase 1 by the time Phase 2 is commissioned. Therefore, additional working capital for commissioning of the second DMS line as well as certain deferred capital expenditures may potentially also be covered by the internal cash flow generation of the business.
According to the PEA, Phase 2 could potentially double total estimated NPV of the Project to US$844 million:
- NPV of Phase 2 Production is estimated to be US$449 million by the PEA.
- NPV of Phase 1 Production is estimated to be US$395 million by the 2019 Feasibility Study Report (calculated with price curves starting from US$650/t in 2021, below current market prices at CIF China port, and operational expenditures reductions limited by the sensitivity analysis in 2019 to be 20%, despite Brazilian currency devaluation since 2019 of approximately 35%)
Barreiro, the Project’s second deposit, has a similar exceptional mineralization to the Project’s first deposit, Xuxa, with large crystals of coarse spodumene. As a result, the lithium achieves outstanding recoveries in an environmentally friendly DMS plant, with similar flowsheet (and capital costs) to the first production line, without requiring a significantly more capital-intensive flotation process.
During Detailed Engineering for Phase 1, the Company evaluated operational and capital expenditure trade-offs to be achieved in the expansion of the Production Plant capacity, including design features to allow for the seamless incorporation of a second production line.
Metallurgical HLS tests performed on the spodumene ore for Phase 2 in sizes of 6.3mm and 10mm achieved excellent lithium recoveries of 70.2% and 66.1%, respectively, producing a 6% Li2O battery-grade spodumene concentrate within the highest levels of specifications demanded by the chemical lithium market without the use of flotation or hazardous chemical reagents, in the concentration process. This is consistent with Sigma’s intention to continue to process its lithium ore in a “green” environmentally friendly and sustainable manner.
The Company has been working with SGS and Primero to prepare a PFS for the Phase 2 production, targeting its completion in June 2021, further continuing towards feasibility analysis in the second half of 2021. The Company and Primero completed all the metallurgical and variability DMS pre-feasibility test work at SGS laboratories.
The Project is located in one of the world’s largest mining provinces in southeast of Brazil: with full mining infrastructure and highways linking the Project to a commodities shipment capable port. Site infrastructure has been mostly in place and is currently being upgraded for Phase 1 production. The Project is powered by 100% clean energy: transmission towers and lines on site link the Project to a hydroelectricity plant 50km away.
SIGMA PHASED PRODUCTION APPROACH FOR THE PROJECT AND COMMERCIAL STRATEGY
As a result of the substantial size of its mineral resources, the Company has sub-divided the development of the Project into an incremental and phased build-out.
Sigma is working to advance Phase 2 to a construction ready status by the end of 2021 or early 2022. Phase 2 construction is projected to commence once the commissioning and production ramp up of Phase 1 is completed, which is expected in the third quarter of 2022.
This phased approach to development of the Project increases financial flexibility and reflects the Company’s ethos and discipline in managing construction risk, while seeking to create substantial shareholder value. It also reduces commercial risk by aligning commercial integration of the Project’s production growth profile with the demand of its customers in the lithium-ion battery supply chain.
As a result of the high quality and low impurities of its lithium products, the Company has experienced significant commercial success with various customers in the electric vehicle supply chain. As a result, the Company made a decision to accelerate the required studies for the development of Phase 2, to potentially respond to a significant increase in demand from its customers, following the significant improvement in the outlook of global demand for ESG-sustainable lithium products.
By demonstrating its ability to expand production in the near term, the Company seeks to take advantage of the current strong demand, and solidify its unique commercial advantage in delivering environmentally, socially sustainable and low carbon high purity lithium products to like-minded cathode and battery producers.
The technical report for the PEA will be filled on SEDAR (and will also be available at www.sigmalithium resources.com within 45 days of this news release. Readers are encouraged to read the technical report in its entirety, including all qualifications and assumptions related to the PEA results announced in the news release.
FIRST QUARTER 2021 RESULTS: PHASE 1 CONSTRUCTION & PROJECT DEVELOPMENT UPDATE
The Company has reported unaudited financial and operating results for the first quarter ended March 31, 2021 (“1Q 2021”). Overall, the Company made significant progress towards construction, despite the circumstances created by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Highlights of Phase 1 construction update include:
- All Detailed Engineering and Pre-Construction workstreams continued to advance to achieve production in the third quarter of 2022.
- At the end of Detailed Engineering, the Project will move to the Implementation/Deployment Stage (FEL 3 / Class 3) in the third quarter of 2021, with increased accuracy from the capital estimates included in the Feasibility Study Report.
- Strict COVID-19 health and safety protocols are in place. Without any cases of COVID-19 reported at site since April 30, 2021.
- Construction site early works are ongoing (clearing and grubbing, laydowns & topsoil removal):
- Followed by additional topsoil removal and foundation preparations, once results and geotechnical modelling of Production Plant foundation are concluded.
- Concluded all field Pre-Construction activities for the Production Plant.
- Primero conducted a review of the current designs, assessing the impact on the foundation design and earthwork quantities, based on the geotechnical assessment for the civil engineering and concluded that the soil condition does not create any risk for construction of the foundations of the Production Plant.
- Completed trade-off studies for the optimization and expandability/scalability of the overall plant design, evaluating multiple design options, performing tests and analysis to select the preferred option.
- Expansion design features are being determined in order to allow for the incorporation of a second production line for Production Phase 2.
- Concluded the definition of the streamlined scope and design of the non-process, non-plant infrastructure (building infrastructure).
- Completed several critical workstreams involved in the Pre-Construction of the Phase 1 Mine within the scheduled and budgeted parameters.
- This includes all field-based activities required for the geotechnical validation at detailed engineering level, as well as critical field work of hydrogeological validation.
- All remaining state permits required to commence construction are forecasted to be issued by the third quarter of 2021.
Highlights of ESG:
- Significantly advanced the life cycle analysis and carbon credits audit workstreams, planning to publish results in the third quarter of 2021, including more information on its carbon in-setting and offsetting strategy.
- Continued to progress on the creation and structuring of an independent agency for private investment promotion and economic diversification of the region (“Investment Agency”), with institutional support from the development bank of the state of Minas Gerais (“BDMG”), from the secretary of special development projects (“INDI”) and from the Mayors of the two municipalities.
- Expanded humanitarian relief during the months of COVID-19 pandemic for the population living in extreme vulnerability in the region, as follows:
- Distributed 1,200 basic food baskets in two months, feeding approximately 2,400 people per month.
- Agreed to extend the initiative in a collaboration with Rotary Club, distributing an additional 1,000 food baskets (feeding an additional 4,000 people).
- Repeated COVID-19 prevention initiatives from March 2020, and distributed 12,000 units of hospital disinfectant, as well as 2,400 hand sanitizers “family size”, totaling 840 kg of the product.
- Initiatives funded at cost as a result of financial sponsorship from Sigma’s key shareholders and stakeholders.
Corporate:
- As at the date of this MD&A, the Company has $41.3 million (US$33.6 million) in cash and cash equivalents, out of which approximately $33.8 million (US$28 million) is held in a construction segregated savings account.
- Additionally, it has an undrawn credit line balance of US$4,037,150 under the US$5,000,000 unsecured revolving credit facility (the “A10 Credit Facility”)
- The Company has announced that it is considering a potential listing of the Common Shares in a major U.S. stock exchange market with a view to increasing access to U.S. capital markets and enhancing overall shareholder value.
- Consistent with its retention policies to manage human capital as well as with its ethos of aligning incentives amongst all stakeholders and shareholders, most of the compensation of the Company’s key personnel is equity based.
- To that regard, the Company grated an aggregate of 996,333 Restricted Share Units to officers and an aggregate of 385,000 Restricted Share Units to key employees and consultants. As per the ESOP, Ana Cabral-Gardner and Calvyn Gardner were not awarded equity compensation.
Calvyn Gardner, Sigma CEO said that “We continue to progress updating the current Feasibility Study Report with the pre-feasibility for the Phase 2, which would be fully integrated into the production complex for the Phase 1, currently in pre-construction. The previous work undertaken when completing our 2019 Feasibility Study Report, as well as detailed engineering phase of pre-construction for Phase 1, means that substantial plant engineering design as well as mining cost databases are available to support the technical studies required for this update, expediting and de-risking its execution.”
Ana Cabral-Gardner, Sigma President and Chief Operating Officer stated that “The doubling of Sigma’s near-term planned capacity to 66,000 LCE, with low additional capex has the potential to significantly transform our scale and relevance. It further increases our uniqueness as a global supplier of environmentally sustainable green lithium concentrate, while consolidating our strategic importance upstream as a source of high-purity green lithium products for our current and new customers, as they advance their plans for cathodes and battery cell production facilities in Europe and the United States, effectively building a sizable Atlantic lithium supply chain”.
Figure 1a: Plant 3D layout of the industrial complex and production facility for Phase 1 and Phase 2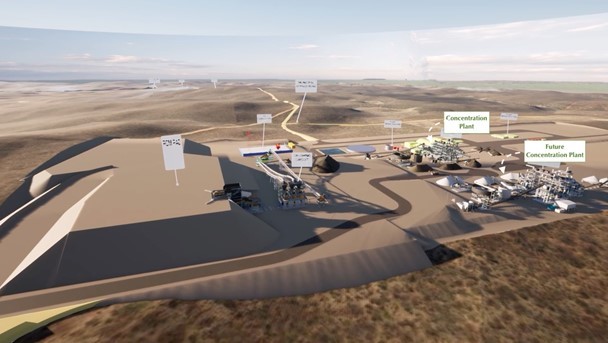
Figure 1b: Plant 3D layout of the industrial complex and production facility for Phase 1 and Phase 2
1 - SUMMARY OF PROJECT FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE RESULTS
1.1 Project Economics
An economic analysis for Phase 2 was developed using the discounted cash flow method and was based on the data and assumptions for capital and operating costs for mining, processing and associated infrastructure. The basis for forecasted spodumene concentrate lithium pricing was provided by Roskill’s arm’s length price curve with an internal adjustment starting with 2022 price of US$750/t (below current 2021 spot market). Although approximately 70% of the Company’s operational costs are incurred in Brazilian reais, the assumptions were fixed in USD, the base currency for the financial model. Key assumptions and results of the economic evaluation are displayed in the tables 1 and 2 below.
Table 1.1.1: Financial Results Summary for Phase 2 During the Estimated Life of Mine
| Financial Summary | Unit | Total |
| Net Present Value (NPV 8%) After-Tax | US$ M | $449 |
| Internal Rate of Return (IRR) After-Tax | % | 208% |
| After-Tax Payback Period | Years | 0.4 |
| Capital Intensity (Initial Capex/ Annual Production) | US$ per tonne | $200 per tonne |
| NPV: Capex (ratio) | Ratio X:1 | 10:1 |
Table 1.1.2: Key Assumptions Utilized in the Project Economics
| Assumptions | Unit | Total |
| Annual Lithium Concentrate Production at 6% | tonnes | 222,147 |
| Project Estimated Life (Integrated Mine/Plant) | years | 12.7 |
| Discount Rate | % | 8 |
| Total Royalty (1) | % | 3 |
| Average Corporate Tax (2) | % | 15.3 |
| CAPEX | ||
| Year 0 (plant construction and starter mining pit) | US$ M | 44.5 |
| Year 5 (pit expansion) | US$ M | 28.9 |
| Year 6 (pit expansion) | US$ M | 9.7 |
| OPEX | ||
| Average total cash cost (FOB Plant) | US$/t | 256 |
| All-in sustaining cost (“AISC”) CIF China | US$/t | 360 |
| Average Selling Price | US$/t | 750 |
(1) CFEM and NSR#1 Royalties
(2) Sudene Corporate Tax Benefit During 8 first years. 34% for the following years
Table 1.1.3: Phase 2 Estimated Revenue, Operating Costs and EBITDA
| Production: Total tonnes of lithium concentrate | 2,870,444 tonnes | ||
| Average Price for project life | $750/t | ||
| Annualized US$ M | Total US$ M | ||
| Gross Revenue | $ 170 | US$ 2,153 | |
| Less: Total Royalties | ($5) | ($61) | |
| (-) CFEM | ($3) | ($43) | |
| (-) Net Smelter Royalties | ($1) | ($18) | |
| Net Revenues | $165 | $2,092 | |
| Less: Site Operating Costs | ($84) | ($1,066) | |
| (-) Mining | ($45) | ($571) | |
| (-) Processing | ($12) | ($156) | |
| (-) Selling, General & Administration | ($1) | ($8) | |
| (-) Transportation Costs | ($24) | ($299) | |
| (-) Depreciation | ($2) | ($32) | |
| EBIT | $81 | $1,026 | |
| % EBIT Margin | 49% | 49% | |
| (+) Depreciation | $2 | $32 | |
| EBITDA | $83 | $1,058 | |
| % EBITDA Margin | 51% | 51% | |
| (-) Taxes | ($16) | ($203) | |
| (+/-) WC | ($0) | ($3) | |
| (-) Capex | ($7) | ($85) | |
| After-Tax Free Cash Flow | $60 | $767 | |
| % Margin | 37% | 37% | |
1.2 - Capital and Operating Costs
SGS and GE-21 completed the Class 5 estimate (+/- 30%) of the capital and operating costs, incorporating engineering from the ongoing detailed engineering and FEED (front end engineering design) of Sigma’s Phase 1 Production Plant. The Capex has been prepared to reflect optimized site layouts, mine scheduling, plant and equipment design and installation. Phase 2 development significantly leverages the Production Plant infrastructure that will be constructed for Phase 1. Site infrastructure has been mostly in place (Sigma’s assets are from a brownfield project) and is currently being upgraded for Phase 1.
Operating cost estimates were provided by GE-21 and are based on an owner-operated model and have an accuracy of +/-30 %. The crushing contracting, substation rental, mobile equipment rental and product transport operating costs were incorporated in the overall operating cost.
The cash operating costs were developed based on third party contract mining and outsourced crushing, as well as on the Phase 2 Plant processing cost. The Phase 2 Production is forecasted to have very low operating costs at US$256 per tonne of concentrate as a result of its high grade, high DMS recoveries, low levels of impurities, low cost of electricity and general low country costs. Table 1.2.1 shows the anticipated average operating costs over the LOM. Table 1.1.3 presents the forecast revenue and costs on both a total and average LOM basis.
Table 1.2.1: Operating Cost Estimate
| Cost Category | LOM Average US$/t |
| Mining | $199 |
| Processing | 54 |
| SG&A | 3 |
| Sub-Total | $ 256 |
| Transportation by Truck Mine to Port | 34 |
| Shipping to China Port (average) | 70 |
| Sub-Total | 104 |
| Total | $ 360 |
The CAPEX has been prepared to reflect optimized site layouts, mine scheduling, plant and equipment design, supply and installation. Phase 2 development significantly leverages the plant infrastructure that will be constructed for Phase 1. Site infrastructure has been mostly in place (Sigma’s assets are from a brownfield project) and is currently being upgraded for Phase 1.
The Company has evaluated operational and capital expenditure trade-offs to be achieved as a result of possible design alternatives for the crushing circuit to be installed at the Production Plant. These trade-offs aim to further de-risk and optimize the construction of the Production Plant. The scalability of the Production Plant was also studied to determine expansion design features to allow for the incorporation of a second production line for Phase 2 high-grade green lithium production.
The total initial development CAPEX for Phase 2 is estimated to be US$ 44.5 million. The estimate is detailed in Table 1.2.2 and includes processing, mine equipment purchases, infrastructures, contingency and other direct and indirect costs. Incremental expenditures of US$28.9 million (additional waste mine stripping in year 5) and US$9.6 million (additional waste mine stripping in year 6) can be funded by internal cash flow generation.
Table 1.2.2 Summary of Capital Costs Estimates and Operating Cost Infrastructure Phase 2
| Capex Item (US$ Thousands) | Year 0 | Year 5 | Year 6 | MC |
| Processing Line (Plant) | 29,884 | – | – | – |
| Plant Additional Infrastructure | 6,959 | – | – | – |
| Owners Cost | 1,172 | – | – | – |
| Mine Preparation & Infrastructure | 6,511 | – | – | – |
| Further Opening of Mining Pit (Year 5) | – | 28,975 | – | – |
| Further Opening of Mining Pit (Year 6) | – | – | 9,658 | – |
| Mine Closure | – | – | – | 2,180 |
| Total Capex (Phase 2) | 44,527 | 28,975 | 9,658 | 2,180 |
Table 1.2.2 Detailed Capital Costs Estimates for Second Line Plant and Infrastructure
| AREA | DIRECT | INDIRECT | CONTINGECY | RECOVERABLE | TOTAL | ||||||
| (USD) | (USD) | (USD) | (USD) | (USD) | |||||||
| PROCESSING PLANT | |||||||||||
| 010 - Engineering, Procurement and Management | – | 2,562,000 | 384,000 | (88,000 | ) | 2,858,000 | |||||
| 015 - Commissioning | – | 1,096,000 | 164,000 | (30,000 | ) | 1,230,000 | |||||
| 030 - Vendor Representatives | – | 114,000 | 18,000 | (1,000 | ) | 131,000 | |||||
| 040 - Construction Indirects - Contractors | – | 1,722,000 | 258,000 | (35,000 | ) | 1,945,000 | |||||
| 200 - Process Plant Overall | 130,000 | – | 12,000 | (24,000 | ) | 118,000 | |||||
| 220 - Contract Crushing | 4,044,823 | – | 621,545 | 4,666,368 | |||||||
| 310 - DMS | 13,853,000 | – | 1,694,000 | (2,173,000 | ) | 13,374,000 | |||||
| 314 - Ultrafines DMS | 2,599,000 | – | 305,000 | (401,000 | ) | 2,503,000 | |||||
| 340 - Concentrate Handling | 1,014,000 | – | 110,000 | (110,000 | ) | 1,014,000 | |||||
| 350 - Tails Handling | 1,945,000 | – | 197,000 | (290,000 | ) | 1,852,000 | |||||
| 370 - Process Plant Services | 194,000 | – | 23,000 | (24,000 | ) | 193,000 | |||||
| Subtotal Processing Plant | $ | 23,779,823 | $ | 5,494,000 | $ | 3,786,545 | $ | (3,176,000 | ) | $ | 29,884,368 |
| SITE INFRASTRUCTURE | |||||||||||
| 010 - Engineering, Procurement and Management | – | 1,662,000 | 22,000 | (30,000 | ) | 1,654,000 | |||||
| 020 - Subconsultants | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| 040 - Construction Indirects - Contractors | – | 293,000 | 5,000 | (11,000 | ) | 287,000 | |||||
| 120 - Bulk Earthworks | 2,220,300 | – | 263,100 | (75,900 | ) | 2,407,500 | |||||
| 370 - Process Plant Services | 107,000 | – | 7,000 | (16,000 | ) | 98,000 | |||||
| 390 - Plant Buildings | 151,000 | – | 16,000 | (6,000 | ) | 161,000 | |||||
| 600 - Infrastructure | 756,000 | – | 55,000 | (110,000 | ) | 701,000 | |||||
| 620 - Water & Sewerage | 483,000 | – | 52,000 | (45,000 | ) | 490,000 | |||||
| 630 - Infrastructure General | 327,000 | – | 60,000 | (11,000 | ) | 376,000 | |||||
| 650 - Substation | 8,000 | – | 1,000 | – | 9,000 | ||||||
| 660 - Buildings - Admin | 558,000 | – | 18,000 | (19,000 | ) | 557,000 | |||||
| 770 - Mine Mobile Equipment - LME | 60,000 | – | 6,000 | (2,000 | ) | 64,000 | |||||
| 780 - Fuels | 152,000 | – | 14,000 | (11,000 | ) | 155,000 | |||||
| Subtotal Site Infrastructure | $ | 4,822,300 | $ | 1,955,000 | $ | 519,100 | $ | (336,900 | ) | $ | 6,959,500 |
| OWNERS COST | |||||||||||
| 810 - Owners Project Costs | – | 973,000 | 146,000 | (33,000 | ) | 1,086,000 | |||||
| 811 - Owners Temporary Infrastructure | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| 840 - Spares | – | 91,000 | 13,000 | (18,000 | ) | 86,000 | |||||
| Subtotal Owners Cost | – | 1,064,000,0 | 159,000,0 | (51,000,0 | ) | 1,172,000,0 | |||||
| TOTAL CAPEX FOR THE PHASE 2 PRODUCTION PLANT | $ | 28,602,123 | $ | 8,513,000 | $ | 4,464,645 | $ | (3,563,900 | ) | $ | 38,015,868 |
Table 1.2.3 Detailed of Capital Costs Estimates for Phase 2 Mining
| Capex Item (US$) | Year 0 | Year 5 | Year 6 | MC | ||||
| Mine Preparation & Infrastructure | $ 6,511 | – | – | – | ||||
| Further Opening of Mining Pit (Year 5) | – | $ 28,975 | – | – | ||||
| Further Opening of Mining Pit (Year 6) | – | – | $ 9,658 | – | ||||
| Mine Closure | – | – | – | $ 2,180 | ||||
| Total Capex | 6,511 | 28,975 | 9,658 | 2,180 | ||||
1.3 - Sensitivity Analysis
As displayed in Table 1.1.1, the PEA projects potential strong financial outcomes with a pre-tax NPV (discounted at 8%) of US$449 million and IRR of 208%. Table 1.3. analyses the impact on NPV when spodumene pricing and recovery percentages fluctuate.
The Project NPV is most sensitive to movements in the price of spodumene, metallurgical recovery rate of the lithium at the Second Plant. Foreign exchange fluctuations impact operating cash costs (mostly derived from Brazilian Real) and development capital (approximately 70% derived from Brazilian Real prices)
Table 1.3: Sensitivity Analysis: NPV to Price and Recovery
| Sensitivity Matrix | After-Tax NPV (US$ M) | |||||
| Spodumene Price (CIF China) (US$/t) | Recovery (%) | |||||
| 60.4 | % | 66.0 | % | |||
| $ 650 | $ 260 M | $ 320 M | ||||
| 700 | 319 | 384 | ||||
| 750 | 378 | 449 | ||||
| 800 | 437 | 513 | ||||
| 850 | 496 | 578 | ||||
1.4 – Commercial and Offtake Strategies
As a result of the high quality and low impurities of its planned lithium concentrate Sigma has experienced significant commercial success in negotiating offtake agreements with various customers in the electric vehicle supply chain. Sigma entered the offtake negotiations undertaking a long-term view for the growth of the market and decided to replicate the longer term (five years) contract structures practiced by the lithium chemicals with their cathode industry and other customers in the supply chain. Sigma has been negotiating offtake agreements with fixed volumes with a multiyear duration.
Sigma plans to develop Phase 2 following a similar integrated strategy of delivering green lithium chemicals to customers, through tolling partnerships for chemical lithium products. Discussions are underway with a number of interested parties, whereby (similarly to Phase 1 production) Phase 2 Battery Grade Green Lithium Concentrate will be treated at an offsite downstream conversion facility to produce lithium carbonate or lithium hydroxide for its life of mine.
1.5 - Project Schedule
The Company has significantly advanced multiple Project workstreams in geology, geotechnical, metallurgical, environmental and regulatory permitting with the objective of preparing for Phase 2 production after 2023. Sigma is advancing Phase 2 with the goal of being construction ready by the end of 2021. Phase 2 construction is planned to initiate sequentially to the commissioning and production ramp up of Phase 1 (which is expected in summer of 2022).
The Company has been working with SGS and Primero to prepare a PFS for Phase 2 production, further continuing towards feasibility. The Company and Primero completed all the metallurgical and variability feasibility test work at SGS laboratories with the aim of customizing a flowsheet for the second processing line of Phase 2 production with Barreiro. The Company completed all the field work for the PFS, including geotechnical drilling.
The execution plan for Phase 2 of the Project in 2021 focuses on:
- Continuing the engineering activities to complete a PFS and finalize designs, equipment and plant configurations, which is expected to reduce risks and enhance yield;
- Progression of the environmental and regulatory approvals;
- Continued discussions with potential downstream and offtake partners to achieve a fully integrated operation with the battery industry for electric vehicles; and
- Optimizing the capital structure for the Company and obtain debt and equity financing for the capital expenditures for Phase 2.
2 – MINING
GE-21, prepared the mining section of PEA aiming to assess the economic viability of the Phase 2 of the Project. The Barreiro deposit is located in close proximity to the surface with shallow, near surface mineralization ideal for open pit mining. Therefore, the Barreiro deposit will be mined by conventional open pit methods. Mining will require drilling and blasting and mining material will be removed using hydraulic excavators and haul trucks.
Figure 2.1: Plant 3D layout of the industrial complex and production facility for Phase 1 and Phase 2
The mining operating costs in Table 2.1.1 were based on the proposal of U&M Mineração e Construção SA, presented on July 3rd, 2020, for the Phase 1 contract mining of the Xuxa open pit mine. The scope of services refers to the provision of ore and waste handling services involving the drilling & blasting, excavation, loading and haulage of soil and rock, conservation and dust control, and other ancillary activities. Only the cost of ore haulage from the stockyard to the plant was not part of the scope of the U&M proposal, so it was estimated based on GE21’s inhouse database.
Table 2.1: Key Mining Assumptions Utilized in the Project Economics
| Item | Unit | Total |
| Ore Processed | ||
| Total quantity milled (LOM) | Mt | 21.3 |
| Average Annual run of mine (ROM) milled | Mt | 1.68 |
| Strip ratio | ||
| Year 1 | Ratio: | 5.2 : 1 |
| Year 5 | Ratio: | 10.8 : 1 |
| Year 6 | Ratio: | 15.,5 : 1 |
| Run of Mine Costs | ||
| Mining costs per waste and ore mined | [US$/t mined] | 2.3 |
| Processing costs per tonne (ROM) | [US$/t ROM] | 8.6 |
Pit Optimization
The determination of the optimal pit was based on:
- A calculation of the interlocking (nested) of optimal pits using Micromine software;
- Certain technical and economic parameters were used for the generation of the optimal mathematical pit, which consists of the pit that maximizes the value of the enterprise and was obtained through the application of the Lerchs-Grossman algorithm.
- The economic and geometric parameters were defined based first principles, using GE21's database in accordance with projects of similar scale and characteristics. The geotechnical assessment was based on rock quality and visual inspection on undeformed core samples.
- The selection of the minimum optimal pit with enough mineralized material to supply a production of 1.680 Mtpa during LOM.
- All mineralized material was considered in the optimization process, including that classified as inferred.
The sequence of optimal pits was obtained by varying the revenue factor from 10% to 200% with respect to the product's selling price. To determine the evolution of the pits over time, an annual production scale of 1.680 Mtpa of ROM was established.
The waste was divided into: Overburden; Fresh rock; Low grade – Material with a grade below 0.5% LiO2; Percent – Blocks initially assigned as ROM, but with a block factor smaller than 1 (part of the blocks that were not inside the mineralized body); Outside the Model – blocks generated outside the block model box, to cover the entire length of the pit.
Pit Design
The open pit mine design, consists of projecting, based on a selected optimal pit, an operational pit that allows for the safe and efficient development of mining operations.
The preliminary pit design extends approximately 0.92 km NW/SE along strike of the pegmatite mineralization and has an average width of 1.0km. The design is divided into depths of 100m (RL=200m), 220m (RL =100m) and 300m (RL=10m). Mining is scheduled to achieve low waste stripping in the initial years with a gradual increase later in the mine life, as per the table below. The average strip ratio for the LOM plan is 11.6, as follows:
- Year 2: Ratio – 5.2 : 1
- Year 5: Ratio – 8.8 : 1
- Year 6: Ratio – 10.4 : 1
Thus, the operationalized pit contains 20.485Mt of measured & indicated mineral resources and 1.909Mt of inferred mineral resources) and 246.7 Mt of waste rock, leading to an overall stripping ratio of 11.6, and which results in a mine life of approximately 13 years. The table 2.2 below shows the result for the final operational pit that resulted from the mine design activities.
The use of a mixed fleet is planned, with road trucks for haulage the run of mine (“ROM”) and off-road trucks for haulage of waste rock. Thus, the width of the access road to the final pit was maintained at 24 m (off-road truck), apart from the lower pit benches, which are basically composed of ROM. In this region, a width of 10 m was used for the access road. Site preparation including logging, clearing, grubbing and peat/topsoil removal will occur during the project construction phase. Surface mining equipment requirements are based on mining 10m benches.
The economic analysis was based on potentially recoverable resources, utilizing a contract mining fleet of hydraulic excavators, front-end loaders and 100t haul trucks for waste and 40t haul trucks for the ROM, associated with correspondent ancillary equipment. Fleet was sized to meet the planned tonnage requirements to feed the crushing plant at 1.68 Mtpa. Waste rock will be hauled to multiple waste rock and tailings storage facilities and ROM feed material will be hauled to the ROM pad.
Haul trucks will be used to transport tailings from the plant to the proposed waste rock and dry stacked tailings stockpile areas.
Additional mining engineering undertaken during the ongoing PFS 2021 should increase the level of confidence in the current mine plan and will be reported in updated disclosures. GE-21 is leading the preparation of the mine plan, geotechnical program and modelling of the Barreiro deposit.
- The drilling of three new geotechnical orientated core holes and relogging (geotechnically) of 20 selected exploration holes were completed. The Company engaged Comprobe, a specialist engineering service company, to conduct downhole geotechnical surveys using an acoustic televiewer to probe exploration drill holes. These surveys were completed for the new and historic exploration holes.
- The field work required for the hydrogeological section of the PFS has been completed, as well as all water level measurements.
Table 2.2 - Results - Final Operational Pit for Barreiro Deposit
| Pit | Tonnes (MT) | Li2O (%) | Years | ||||||||
| ROM | Overburden | Fresh Rock | Low Grade | Percent | Outside the Model | Total Waste | Stripping Ratio | In Situ | Diluted | LOM | |
| Mathematical | 21.5 | 2.3 | 204.3 | 0.8 | 5.3 | 10.0 | 222.8 | 10.35 | 1.435 | 1.393 | 12.81 |
| Operational | 21.3 | 2.2 | 221.9 | 0.9 | 5.2 | 16.4 | 246.7 | 11.56 | 1.438 | 1.396 | 12.70 |
Figure 2.2 - Final Operational Pit (Ultimate Pit Design).
3 – PROCESSING
Plant Flowsheet Design
Detailed engineering and flowsheet design for the entire Production Plant currently in pre-construction was performed by Primero, an Australian-based engineering company with global development experience. The process design (flowsheet) is based on an annual throughput of 1.5Mt from the crushing plant of mineralized material (already contemplating a loss of 15% occurred during the crushing) to produce a final product grade of up to 6.0% Li2O. The selected process is similar to that utilized at the Production Plant in pre-construction which incorporates a similar flowsheet based on crushing and DMS.
Table 3.1 – Processing Costs and Throughput
| Item | Unit | Total | |
| Spodumene Processed | |||
| Average Annual run of mine (ROM) milled | Mt | 1.68 | |
| Spodumene ore feed grade LOM average | % | 1.44 | |
| Loss on Crushing | % | 15 | |
High Purity Lithium Concentrate Produced | LOM Average | ||
| Average Lithium Concentrate Produced | t | 222,147 | |
| Lithium Recovery Rate | % | 66 | % |
| Lithium Concentrate Grade | % | 6.0 | % |
| Lithium Carbonate Equivalent Produced | tonnes LCE | 33,000 | |
Processing Costs | |||
| Processing costs per tonne | US$/t processed | 8.6 | |
Processing involves a conventional three-stage crushing circuit, followed by a DMS plant. Similar to the Project’s Xuxa Mine (the “Project’s First Mine” or “Xuxa Mine”), the crystal sizes are coarse and therefore grinding and flotation methods are not necessary, contributing to low operating costs. Other sub processes include:
- dewatering, filtration and dry stack tailings disposal system (with waste rock disposal);
- water, air and ancillary services; and
- spodumene concentrate stockpile and dispatch system.
The mineralized material will be fed from the ROM pad to a three-stage crushing plant consisting of a primary jaw crusher, a secondary crusher and tertiary crusher. Prior to entering the DMS cyclones, the material will be mixed with a ferrosilicon slurry, which acts as a densifying medium to enhance the gravity separation of the spodumene. The processing plant is fully automated and the stability of the dense media in the cyclone is digitally controlled by a proprietary algorithm developed by Primero.
Figure 3.1- Plant 3D layout of the industrial complex and production facility for Phase 1 and Phase 2
Final product grade - Metallurgical HLS Test
A metallurgical test program was carried out by SGS Lakefield of Ontario, Canada to determine optimal plant operating recoveries. The metallurgical tests included a heavy liquid separation (“HLS”) test to evaluate the extent to which a gravity-based separation process, or DMS, could successfully recover the lithium from the spodumene ore. HLS is a perfect separation based on the minerals’ specific gravity (“SG”) and confirms that DMS technology can be used.
HLS test work performed on ore sizes of 6.3mm and 10mm achieved excellent lithium recoveries of 70.2% and 66.1%, respectively, producing a 6% Li2O battery-grade spodumene concentrate within the highest levels of specifications demanded by the chemical lithium market without the use of flotation or hazardous chemical reagents, in the concentration process. This is consistent with Sigma’s intention to continue to process its lithium ore in a “green” environmentally friendly and sustainable manner.
The DMS performance and separation efficiency is done in a pilot plant to simulate a real industrial environment. The DMS test work was conducted on the same sample and achieved similar recoveries (applied to the sensitivity analysis).
The results indicate that the material from Barreiro, the Project’s second deposit, can be processed, purified and concentrated in the same flowsheet ore from the Project’s First Mine in the same Production Plant, as designed in the Feasibility Study Report without requiring major flowsheet modifications, and thus, with low additional capex needs. The results of the metallurgical tests validated high recovery levels obtained for lithium utilizing a dense media separation processing circuit with similar flowsheet to the one designed for the Phase 1 Production Plant.
The metallurgical testing was completed from a sample of 1250kg of spodumene ore composited using drill cores representative of the early, middle and late years of the Barreiro deposit
Table 3.2 - Metallurgical Recovery Assumptions from HLS Test Results for Combined Products (10.0mm)
| Size of 10.0mm or less | Weight (%) | Assay (%) | Distribution (%) | ||||
| Li2O | Fe2O3 | K2O | Na2O | Li | Fe2O3 | ||
| Combined concentrate (2.81 SG) | 15.9 | 6.00 | 0.55 | 0.60 | 0.57 | 66.1 | 38.9 |
| Combined tailings (-2.65 SG) | 67.6 | 0.43 | 0.07 | 3.28 | 4.78 | 20.1 | 21.9 |
| Head grade (plant feed grade) | 100.0 | 1.44 | 0.22 | 2.78 | 3.78 | - | - |
4 - MINERAL RESOURCES ESTIMATE (“MRE”) PHASE 2 BARREIRO
The basis for the PEA is the MRE completed by SGS Geological Services and included in the 2019 Feasibility Study Report, which remains unchanged from January 10, 2019. The resource model derived by SGS was used in the development of the PEA. The table below outlines the total Measured, Indicated and Inferred Mineral Resources for the Barreiro deposit.
Table 4.1: Mineral Resource Estimate for Barreiro
| Cut-off Grade (Li2O%) | Category | Tonnage | Average Li2O% |
| 0.5 | Measured | 10,313,000 | 1.4 |
| 0.5 | Indicated | 10,172,000 | 1.46 |
| 0.5 | Measured+Indicated | 20,485,000 | 1.43 |
| 0.5 | Inferred | 1,909,000 | 1.44 |
- The mineral resource estimate was conducted using the 2014 CIM Definitions Standards for mineral resources in accordance with National Instrument 43-101, Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects. Mineral resources, which are not mineral reserves, do not have demonstrated economic viability. Inferred mineral resources are exclusive of the Measured and Indicated resources.
- A fixed density of 2.71 t/m3 was used to estimate the tonnage from block model volumes.
- Resources are constrained by the the topography
- Geological CoG estimated from Li2O values of the composite vs value in block
5 - ENVIRONMENTAL AND SOCIAL IMPACTS
5.1 – Environmental
The Company has ongoing comprehensive environmental and social programs in process, consistent with its leadership role in ESG in the lithium mining sector and its commitment to sustainable mining. The mitigating social and environmental programs already initiated or to commence during construction phase aim to establish actions to proactively mitigate, prevent, control and compensate for the environmental impacts that could be caused by the mining activity to be carried out by the Company once it enters the production phase.
Starting in the dry season of the second quarter of 2020, the Company has been conducted detailed environmental impact studies for the fauna and the flora in the area of the Barreiro deposit where the pit and waste piles will be located. These studies continued in the wet season during the third and fourth quarters of 2020. The environmental impact studies were completed and a comprehensive environmental and social impact assessment report (EIA/RIMA) was prepared and concluded by the Company. The design proposed by the Company in the EIA/RIMA for the ADA (Directly Impacted Area by the Project) has followed the Company’s ESG-centric approach to minimize vegetation suppression and contemplated the location of its processing tailings dry stacking piles in the vicinity of the Production Plant with the selection of areas for waste piles targeting the overall minimization of vegetation and tree suppression which, in combination with the vegetation suppression required for the pit areas, amounts to less than 50 hectares. As a result, the life cycle analysis of the Company is substantially enhanced, decreasing its mining carbon footprint.
Once the EIA/RIMA is submitted and approved by regulators, additional ancillary construction and operation permits from environmental authorities will be required prior to construction.
5.2 - Social
The Project is located in one of the poorest regions of Brazil, the Vale do Jequitinhonha, and within two municipalities: Itinga and Araçuaí. These towns are located 17km from the Project site and are the nearest major communities to the site.
The Company, as part of its ESG-centric strategy of shared gains and value creation with the communities around the Project, has determined as a core social objective the principles and guidelines of UN-SDG #8 of “decent work and economic growth”. The Company is committed to achieve this by strengthening the regional socioeconomic environment within the two municipalities where it operates in the Vale do Jequitinhonha. Sigma has a strong working relationship with both municipalities and its communities and conducts regular and meaningful engagement and consultation with them
Also following the principles and guidelines of UN-SDG #17 “partnership for the goals”, the Company initiated a project to lead the creation, structuring and operation of an independent agency for private investment promotion and economic diversification of the region (“Investment Agency”). This workstream was divided in two stages.
- Stage 1, which is expected to be completed by the third quarter of 2021 is to provide the framework for the Investment Agency, including: (i) mapping and approaching stakeholders, (ii) evaluation of the region's “maturity” and “economic engagement” indices, (iii) definition of the Agency Model for the region, (iv) consolidation of governance and management models, (v) modulation of the economic sustainability plan, (v) modulation of “priority sectors” to attract investments.
- Stage 2 is expected to be implemented over a twelve month period, and include the following activities: (i) structuring legal constitution, building councils, and identifying independent executive leadership, (iii) elaboration of the territory value proposition to attract investments (competitive differentials), (iv) validation of “priority sectors” to attract investments, and (v) execution of the first “territory promotion and facilitation activities”, and (vi) identification of additional regional sponsorship.
On April 29, 2021, in line with the principles and guidelines of UN-SDGs #17 partnership for the goals #1 no poverty and #2 zero hunger, the Company launched an initiative to provide humanitarian relief during the next 10 months of pandemic for the local population living in poverty “Sigma contra a fome” (Sigma against hunger). The initiative will distribute 600 basic food baskets per month to 600 families (with an average of four people), feeding approximately 2,400 people per month. Moreover, the company revived and expanded the COVID-19 prevention initiative from March 2020, and it is distributing 12,000 units of hospital disinfectant, totaling 12 tons, as well as 2,400 hand sanitizers “family size”, totaling 840 kg of the product.
5.3 – Permitting
The Company obtained a key permit for Phase 2 production with the Agência Nacional de Mineração (the “ANM”) approving its economic feasibility study (“Plano Econômico de Avaliação” - PAE). This approval advanced the Phase 2 production permitting process to the mining concession request stage (“Requerimento de Concessão de Lavra”)
The PEA is preliminary in nature and includes inferred mineral resources that are considered too speculative geologically to have economic considerations applied to them that that would enable them to be categorized as mineral reserves. There is no certainty that the PEA results will be realized. Mineral resources that are not mineral reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability.
ABOUT SIGMA LITHIUM
The Company is developing, with an environmental sustainability focused and ESG-centric strategy, the largest hard rock lithium deposits in the Americas, located in its wholly owned Grota do Cirilo Project in Brazil with the goal of participating in the rapidly expanding global supply chain of electric vehicles.
Based on the 2019 Feasibility Study Report, the Company plans to produce 220,000/t annually of battery grade lithium concentrate (33,000 t of lithium carbonate equivalent in Phase 1 production and expects to be amongst the world’s lowest cost producers. In Phase 2 production, if warranted after ongoing feasibility study, production would be increased to 440,000 t (66,000 tonnes of LCE) annually. The first phase of production for the Project will utilize as feedstock spodumene from the Project’s Xuxa deposit. The next production phase of the Project would be increased production including feedstock from the Project’s Barreiro deposit.
Since 2018, the Company has been producing low carbon high purity lithium concentrate at an on-site demonstration pilot plant with the objective to ship samples to potential customers for product certification and testing. This pilot production has been an important part of the successful commercial strategy of the Company allowing it to ship samples of its low carbon “green & sustainable” high purity lithium to leading global potential customers, for product certification and testing.
The Company is in pre-construction and detailed engineering of an environmentally friendly, fully automated, dense media separator production plant that applies proprietary algorithms to digitally control the dense media (the “Production Plant”). The Production Plant will be vertically integrated into the Company ́s mining operations, exclusively utilizing as feedstock the high purity spodumene ore with exceptional mineralogy from the Project. The Production Plant will process the spodumene ore into a high purity 6% battery-grade lithium concentrate engineered to the specifications of its customers in the lithium- ion battery supply chain for EVs.
In order to secure a leading position supplying the clean mobility and green energy storage value chains, the Company has adhered consistently to the highest standards of environmental, social and governance practices, which were established as part of its core purpose at inception in 2012. Its production process will be powered by clean energy and the Company will use state-of-the art water recirculation circuits in its processing combined with dry stacking tailings management. The DMS process of the Production Plant does not utilize hazardous chemicals, as a result its tailings are 100% recyclable into ancillary industries, such as ceramics.
The Company plans to achieve net zero carbon emission targets by 2023, partly as a result of its strategic decision to pursue generation of carbon credits through “in-setting” carbon credits (preserving and developing the agroforestry systems within its regional ecosystem). The Company is currently undergoing an independent assessment of its net carbon footprint, conducting an independent ISO 14000 compliant audit of its life cycle analysis together with an independent expert validation of its carbon credits generated by its internal preservation, reforestation, and compensation forestry programs. The Company expects to complete this workstream in the second half of 2021.
Sigma has significant potential for additional future expansion and growth, as it owns 27 mineral rights spread over 191 km2 (which include mining concessions, applications for mining concessions, exploration authorizations and applications for mineral exploration authorizations). The Grota do Cirilo Project area includes nine past producing lithium mines.
QUALIFIED PERSONS
The technical and scientific information related to geology and mineral resource estimate in this news release has been reviewed and approved by Marc-Antoine Laporte P.Geo., M.Sc., of SGS Geological Services. Mr. Laporte is a Qualified Person as defined by National Instrument 43-101 and is independent of Sigma.
The mining and financial information in this news release has been reviewed and approved by Porfirio Cabaleiro Rodriguez P.Eng, Mining Engineer of GE21 Consultoria Mineral Brazil. Mr Rodriguez is a Qualified Person as defined by National Instrument 43-101 and is independent of Sigma.
FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION PLEASE CONTACT
Ana Cabral-Gardner
(Sao Paulo) +55 11 2985-0089
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This news release includes certain "forward-looking statements" under applicable Canadian securities legislation including statements relating to the ultimate duration, impact and severity of the COVID-19 pandemic (including its impact on financial markets and national and multinational economies generally, and its impact on the growth of the electric vehicle market and other impacts on the demand for lithium products) and other forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are necessarily based upon a number of estimates and assumptions that, while considered reasonable, are subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors which may cause the actual results and future events to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. All statements that address future plans, activities, events, or developments that the Company believes, expects or anticipates will or may occur are forward-looking information, including statements regarding the potential development of resources and drilling plans which may or may not occur. Forward-looking statements and information contained herein are based on certain factors and assumptions regarding, among other things, the ability to complete the Annual Filings and Interim Filings; the market price of the Company's securities, metal prices, exchange rates, taxation, the estimation, timing and amount of future exploration and development, capital and operating costs, the availability of financing, the receipt of regulatory approvals, environmental risks, title disputes, litigation risks, failure of plant, equipment or processes to operate as anticipated, accidents, labour disputes, claims and limitations on insurance coverage and other risks of the mining industry, changes in national and local government regulation of mining operations, and regulations and other matters including the COVID-19 pandemic. There can be no assurance that such statements will prove to be accurate, as actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements. Accordingly, readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. The Company disclaims any intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. For more information on the risks, uncertainties and assumptions that could cause our actual results to differ from current expectations, please refer to our public filings available at www.sedar.com.
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this news release.
Plug Into More Green Stock News
Tap into the pulse of emerging green sectors every morning. Top daily headlines from clean energy, cleantech, cannabis, and sustainable transport stocks:
More Green Stock News
More Green Stock News
| Last Trade: | US$15.66 |
| Daily Change: | 2.15 15.91 |
| Daily Volume: | 9,460,799 |
| Market Cap: | US$1.740B |
November 14, 2025 August 15, 2025 May 14, 2025 May 07, 2025 | |




